In this tutorial, I will introduce the file system of Linux especially the frequently used files and the basic commands that do same thing as GUI operations such as moving, rename, copy, delete files, etc.
File system
Click the File icon on the toolbar, select other location and double click the computer.
You can many folders in the root folder /, the top-most directory in the file system.
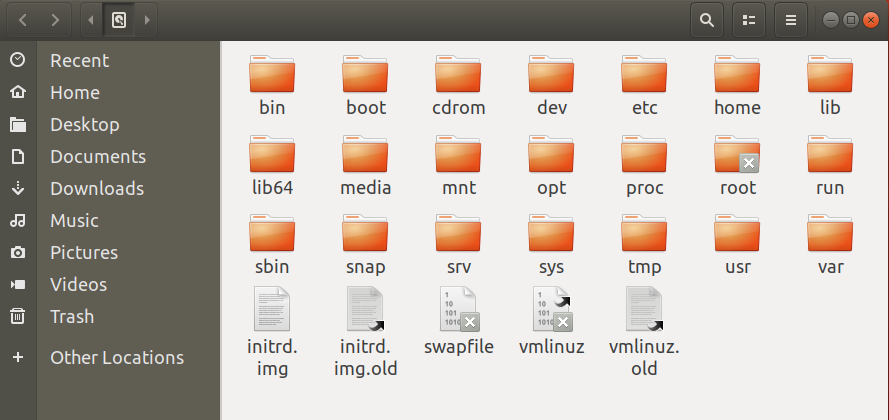
Here I briefly introduce the commonly accessed folder according to my experience.
| folder | full name | description | files |
|---|---|---|---|
| bin | binary files | The folder contains executable files corresponds to the built-in commands in Linux | ls, cd, mv, cp, rm |
| boot | boot | The software (e.g. VMware, Rufus) that write the image file .iso into the bootable system containing this folder |
grub |
| dev | devices | Stores the hardware information | disk, tty |
| etc | et cetra (meaningless) | The system configuration placed | crontab, sudoers, rc.local |
| home | home | Contains the users with Desktop for each | your_name |
| mnt | mount | The folder that mount external devices such as flash drives, SD cards, and even remote folders | — |
| usr | unix system resources | The high-level package relative to OS such as Python | local/lib/python3.6 |
Basic commands
The most important thing to learn operating system is the commands in terminal (it is called CMD in Windows). Press ctrl+Alt+T to open it.
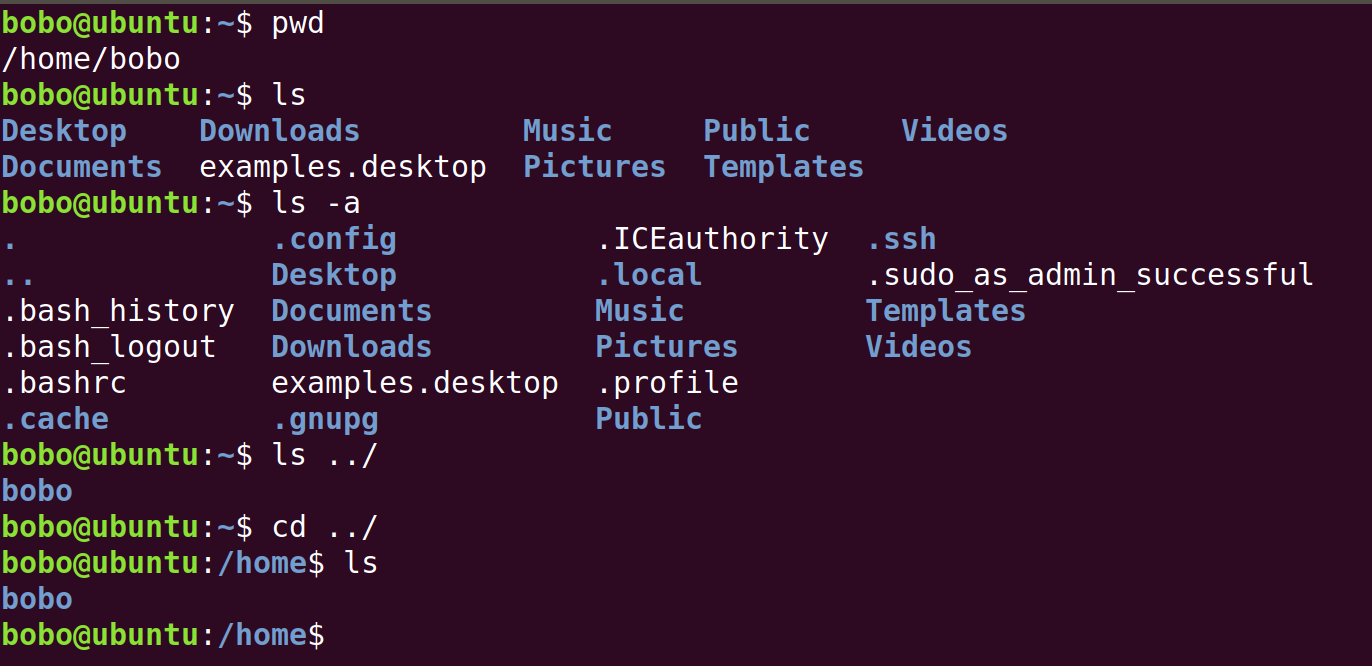
Overview the directories
The commands in the following are the most commonly used.
| Commands | Argument | Description |
| pwd | - | Print Working Directory |
| ls | path (default=current) | listing all the files in the path |
| -a | listing all the hidden files in the path | |
| cd | path | Change directory |
The path in Linux can be relative path, . and ... Here is an example.
Edit and view the text files
You can use ctrl+L in to clean the terminal. There are two commonly-used text editor in Linux, the gedit and the vim. The former is in graphic interface, and the latter will be introduced in the next section.
| Commands | Argument | Description |
| gedit | text file name | New or open a text file for editing |
| cat | text file name | View all the text file |
| head | -n number | View certian lines from the top of the text file |
| tail | -n number | View certian lines from the bottom of the text file |
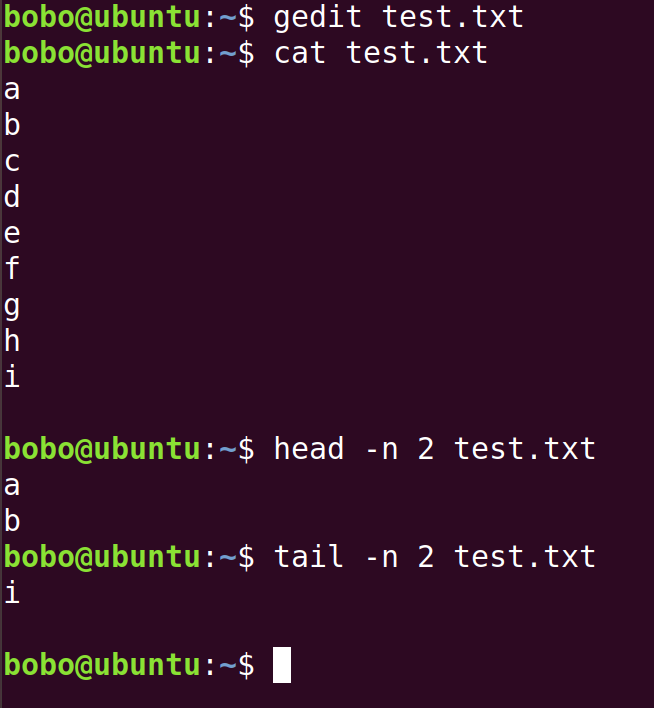
Operations of files and folders
The next part is to learn how to move, copy, rename, create directory.
| Commands | Argument | Description |
| mkdir | folder name | New a folder |
| rm | -r | Remove directory as well as all its children files and folder |
| file name | Remove the file | |
| cp | -r, source path, target path | Copy directory as well as all its children files and folder from the source path to the target path |
| mv | source path, target path (same file name) | Move the file/folder from the source path to the target path |
| source path, target path (different file name) | Move and rename the file/folder from the source path to the target path |
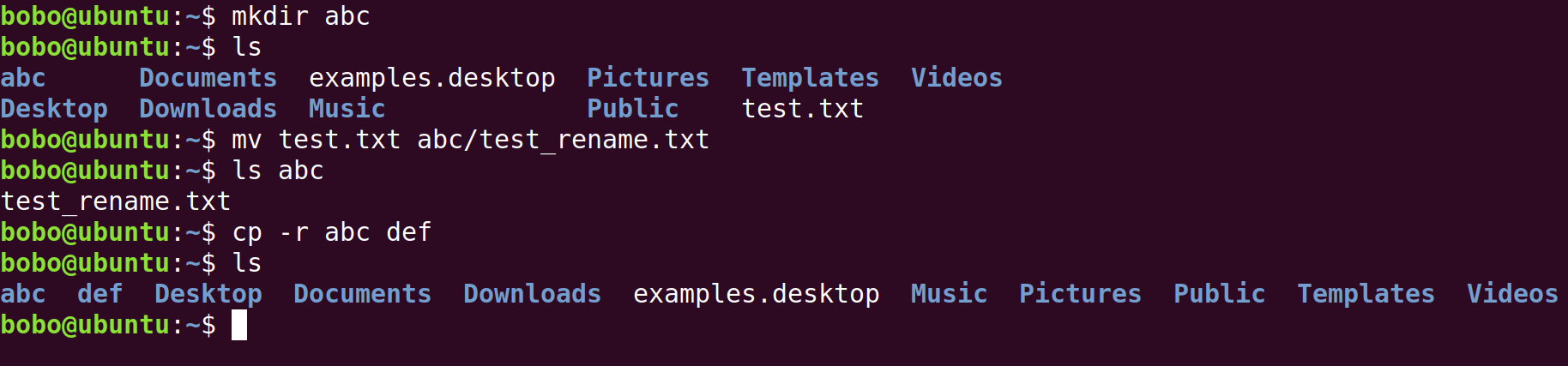
more useful commands
There is at least one user (login by default) and root user in Linux. Some commands are only permit by root only. However, we can borrow the permission with password from root by typing sudo before the command. More on the authorities will be discussed in the next tutorial.
1 | sudo <command> |
For example, the time must be modify thorugh the superuser permission.
1 | sudo date -s "20210214 10:21:32" |
To find a specific string in the output of a consult. Use grep command with pipeline operator |.
1 | <command> | grep <pattern> |
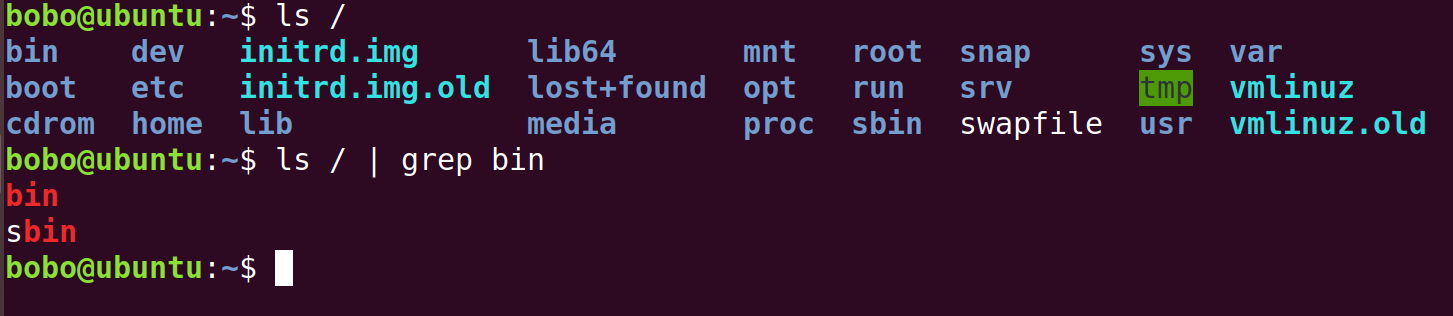
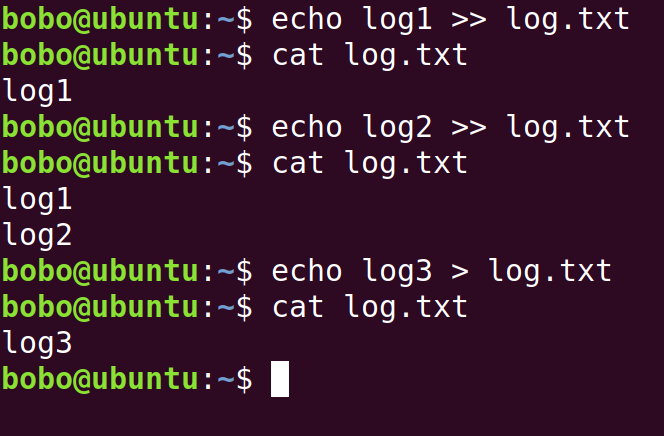
The echo command is to print something such as log. It usually used with > and >>, which are “continue writing” and “overwriting”.
1 | echo <something> >> <text_file> |